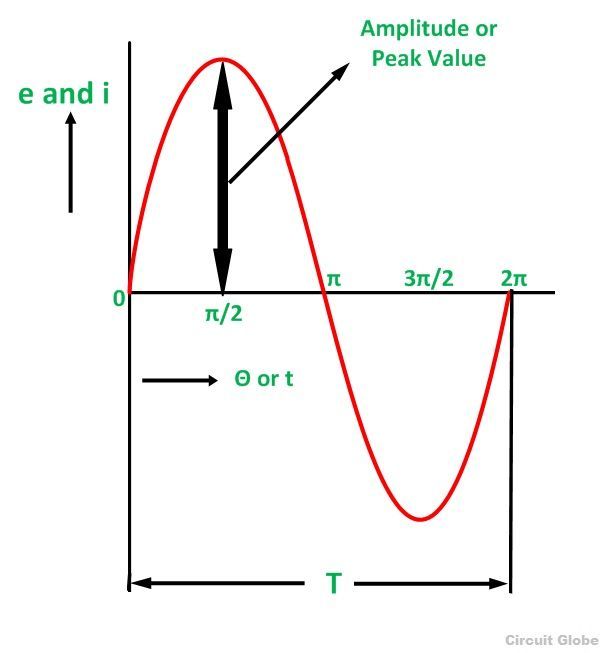
Peak Value
Definition: The maximum value attained by an alternating quantity during one cycle is called its Peak value. It is also known as the maximum value or amplitude or crest value. The sinusoidal alternating quantity obtains its peak value at 90 degrees as shown in the figure below. The peak values of alternating voltage and current is represented by Em and Im respectively.
 Average Value
Average Value
Definition: The average of all the instantaneous values of an alternating voltage and currents over one complete cycle is called Average Value.
If we consider symmetrical waves like sinusoidal current or voltage waveform, the positive half cycle will be exactly equal to negative half cycle. Therefore, the average value over a complete cycle will be zero. The work is done by both, positive and negative cycle and hence the average value is determined without considering the signs.
So the only positive half cycle is considered to determine the average value of alternating quantities of sinusoidal waves. Let us take an example to understand it.
Let i1, i2, i3…….. in be the mid ordinates
The Average value of current Iav = mean of the mid ordinates
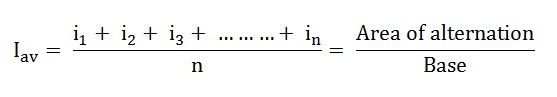 R.M.S Value
R.M.S Value
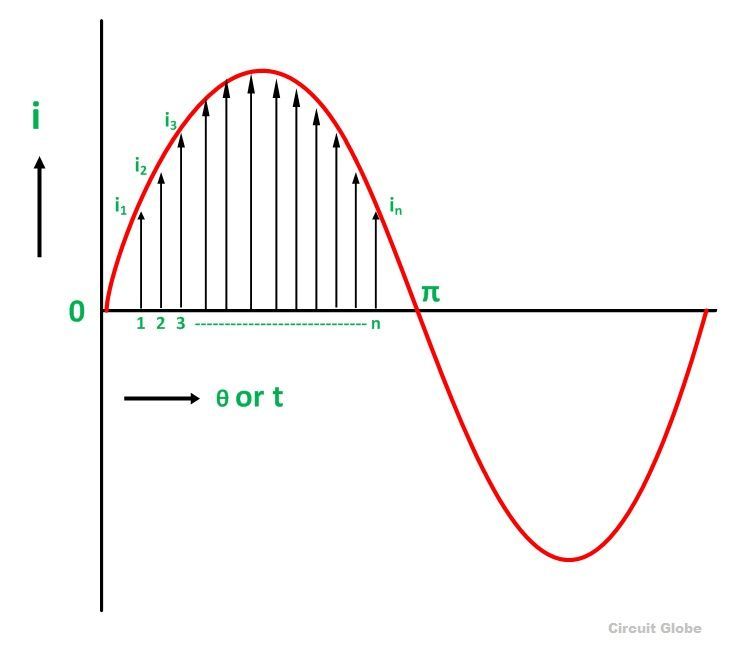
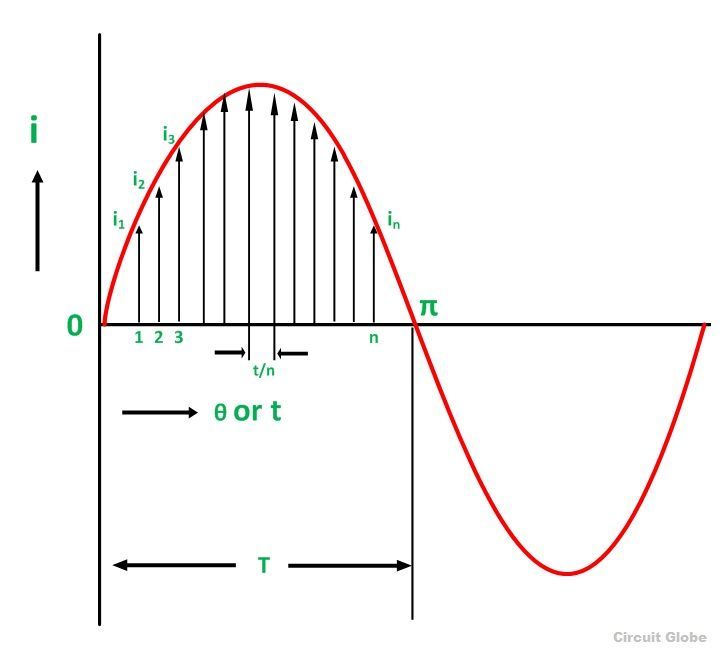
Definition: That steady current which, when flows through a resistor of known resistance for a given period of time than as a result the same quantity of heat is produced by the alternating current when flows through the same resistor for the same period of time is called R.M.S or effective value of the alternating current.
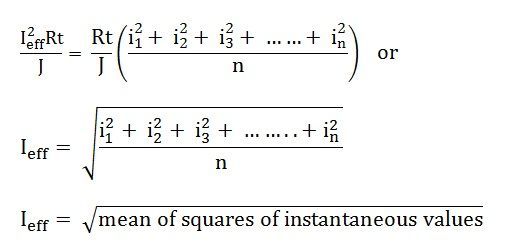
In other words, the R.M.S value is defined as the square root of means of squares of instantaneous values.
Let I be the alternating current flowing through a resistor R for time t seconds, which produces the same amount of heat as produced by the direct current (Ieff). The base of one alteration is divided into n equal parts so that each interval is of t/n seconds as shown in the figure below.
Then the heat produced in
 Since Ieff is considered as the effective value of this current, then the total heat produced by this current will be
Since Ieff is considered as the effective value of this current, then the total heat produced by this current will be
Ieff = square root of mean of squares of instantaneous values = R.M.S value
Root Mean Square is the actual value of an alternating quantity which tells us an energy transfer capability of an AC source. The ammeter records the RMS value of alternating current and voltmeter record’s the root mean square (R.M.S) value of alternating voltage. The domestic single phase AC supply is 230 V, 50 hertz, where 230 V is the R.M.S value of alternating voltage.
The values of voltage and the current system in a DC circuit is constant, so there is no issue in evaluating their magnitudes, but in an AC system, the alternating voltage and current vary from time to time and hence it is necessary to evaluate their magnitudes. The following three ways (peak value, Average value and R.M.S value) given above are adopted to express the magnitude of the voltage and current.
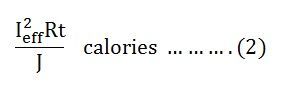



0 Comments